Slack++ - Built with AI to power work
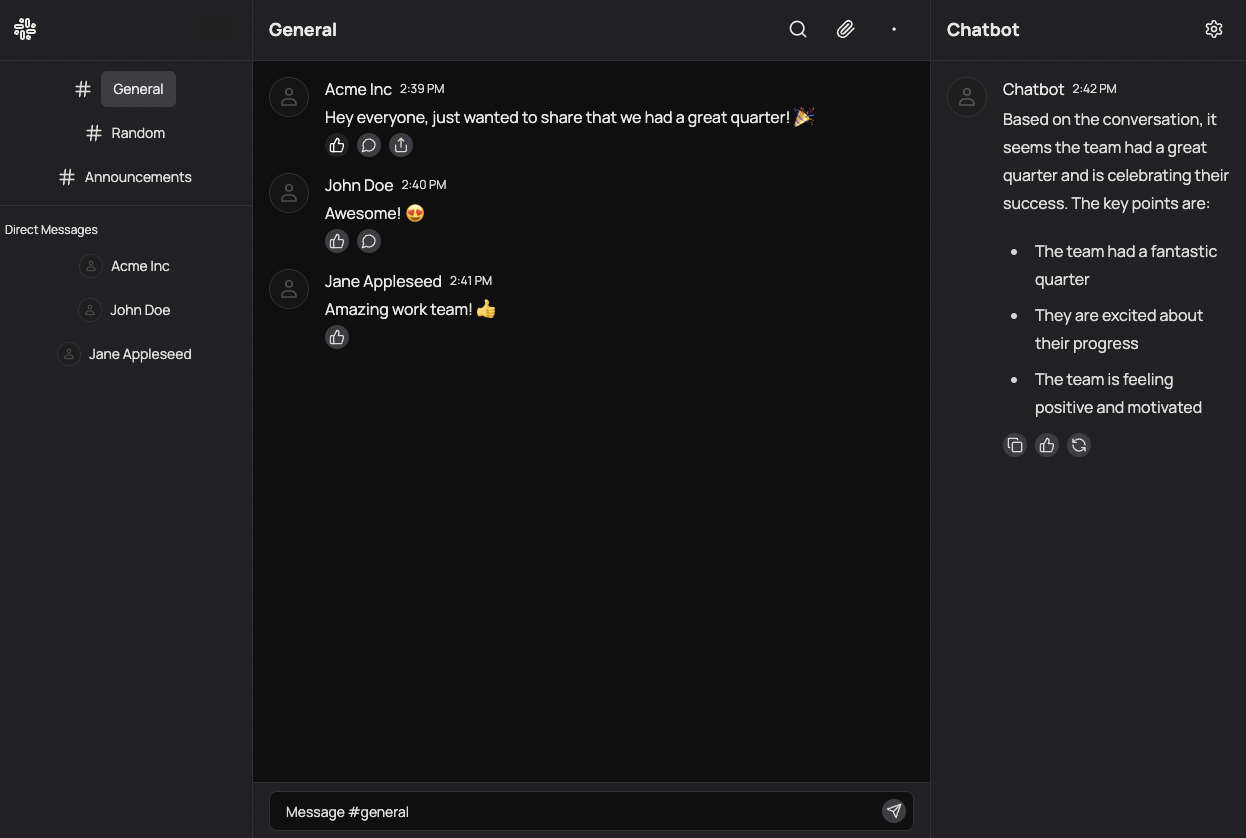
Slack++ is a multitenant application designed to provide a robust messaging platform similar to Slack but with additional AI-powered features. The primary tenants of this system are organizations, each identified by a tenant_id. The key features include:
- Channels: Users can create and join channels to facilitate team communication.
- Messages: Users can send and receive messages within channels.
- Direct Messages: Users can communicate privately with one another.
- AI Summarization: The AI system can summarize conversations within channels.
- Message Search: Users can search for messages within a channel and across channels.
- Theme Highlighting: The AI chatbot can highlight themes from discussions in a channel.
- User Management: Manage users and their membership in channels.
Each table will include tenant_id as part of its primary key, and all IDs will be of type UUID.
Postgres Schemas
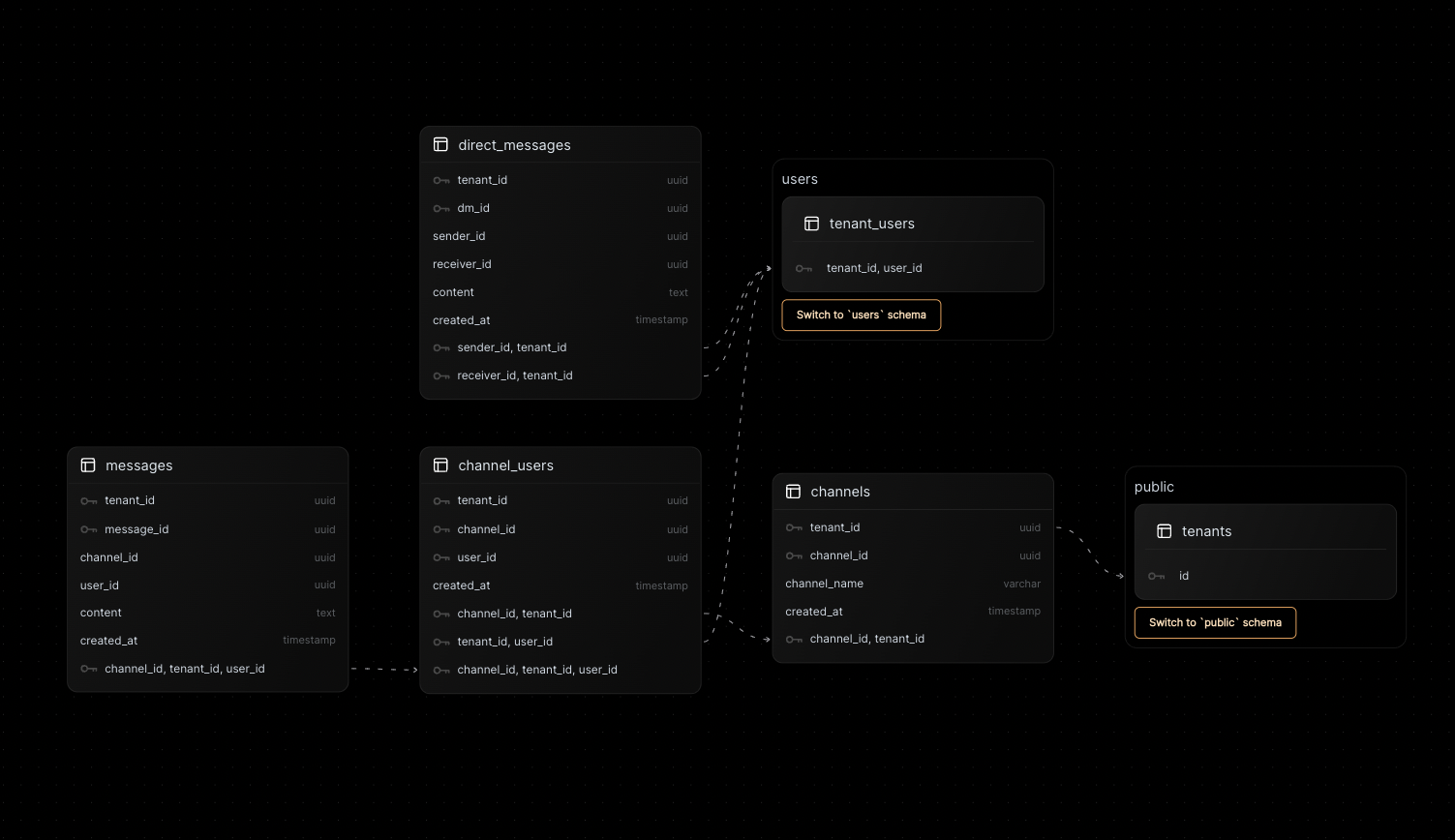
Note that the tenants, users and tenant_users tables references in these schemas are already built-in within Nile's Postgres database.
1. channels
Stores channel information for each tenant. Users can be part of multiple channels and conversation happens within channels.
CREATE TABLE channels (
tenant_id UUID,
channel_id UUID DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
channel_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, channel_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id) REFERENCES tenants(id)
);
2. channel_users
Maps users to channels within a tenant. The users within a tenant can be part of multiple channels.
CREATE TABLE channel_users (
tenant_id UUID,
channel_id UUID,
user_id UUID,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, channel_id, user_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, channel_id) REFERENCES channels(tenant_id, channel_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, user_id) REFERENCES tenant_users(tenant_id, user_id)
);
3. messages
Stores messages within channels along with vector embeddings for AI functionalities. Note that this example calculates embeddings for each message. In practice, you would not do this since it would blow up the number of embeddings and lack full context. A better option is to chunk the messages around a time range into one embedding. You could optionally have a messagechunk table that track each chunk and stores embeddings for them.
CREATE TABLE messages (
tenant_id UUID,
message_id UUID DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
channel_id UUID,
user_id UUID,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
vector_embedding VECTOR(768), -- Adjust the dimensions as needed
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, message_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, channel_id) REFERENCES channels(tenant_id, channel_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, user_id) REFERENCES tenant_users(tenant_id, user_id)
);
4. direct_messages
Stores private messages between users along with vector embeddings for AI functionalities. Like the messages table, you would want to use a chunking approach for messages.
CREATE TABLE direct_messages (
tenant_id UUID,
dm_id UUID DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
sender_id UUID,
receiver_id UUID,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
vector_embedding VECTOR(768), -- Adjust the dimensions as needed
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, dm_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, sender_id) REFERENCES tenant_users(tenant_id, user_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, receiver_id) REFERENCES tenant_users(tenant_id, user_id)
);
These schemas provide the foundation for a multitenant Slack++ application with AI features, ensuring each table follows the multitenant structure with tenant_id and uses UUIDs for primary keys. The vector_embedding column is included in the messages and direct_messages tables to support AI functionalities like summarization and search.
Full Script
-- Create channels table
CREATE TABLE channels (
tenant_id UUID,
channel_id UUID DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
channel_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, channel_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id) REFERENCES tenants(id)
);
-- Create channel_users table to map users to channels within a tenant
CREATE TABLE channel_users (
tenant_id UUID,
channel_id UUID,
user_id UUID,
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, channel_id, user_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, channel_id) REFERENCES channels(tenant_id, channel_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, user_id) REFERENCES tenant_users(tenant_id, user_id)
);
-- Create messages table with vector embedding for AI functionalities
CREATE TABLE messages (
tenant_id UUID,
message_id UUID DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
channel_id UUID,
user_id UUID,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
vector_embedding VECTOR(768), -- Adjust the dimensions as needed
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, message_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, channel_id, user_id) REFERENCES channel_users(tenant_id, channel_id, user_id)
);
-- Create direct_messages table with vector embedding for AI functionalities
CREATE TABLE direct_messages (
tenant_id UUID,
dm_id UUID DEFAULT gen_random_uuid(),
sender_id UUID,
receiver_id UUID,
content TEXT NOT NULL,
vector_embedding VECTOR(768), -- Adjust the dimensions as needed
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
PRIMARY KEY (tenant_id, dm_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, sender_id) REFERENCES tenant_users(tenant_id, user_id),
FOREIGN KEY (tenant_id, receiver_id) REFERENCES tenant_users(tenant_id, user_id)
);